Type I Interference
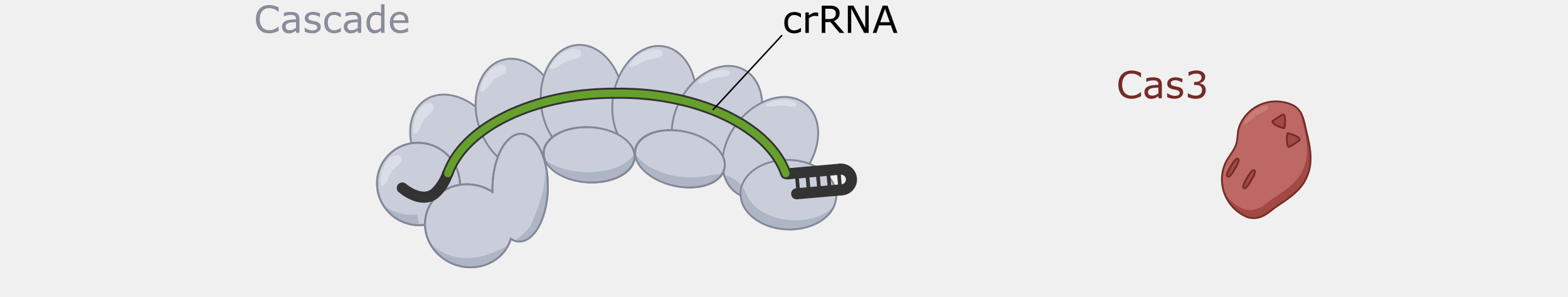
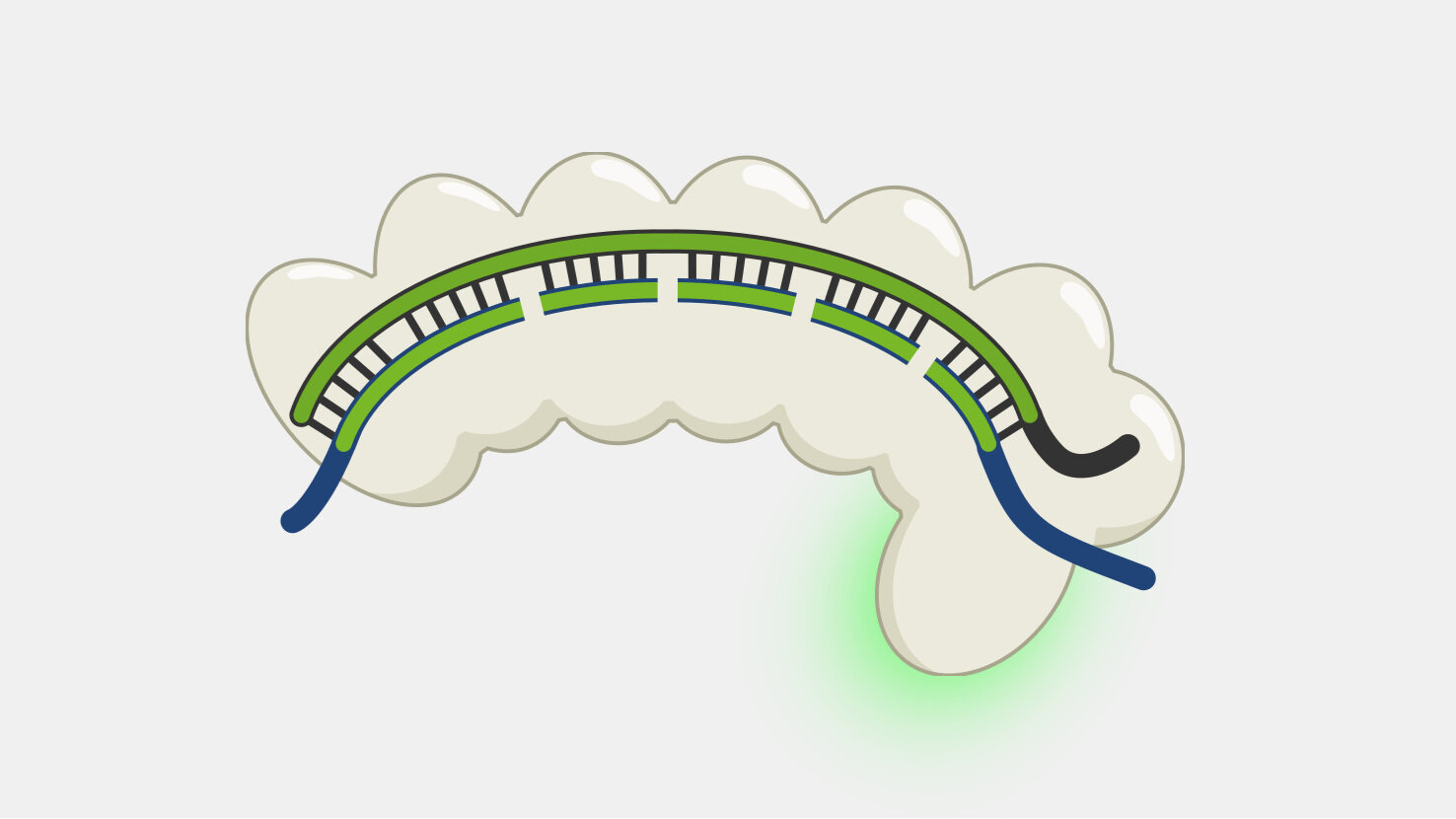
Type I systems are the most wide-spread CRISPR systems in nature. Like the more-well known Type II systems, Type I systems provide immunity by specifically degrading phage DNA. Type I systems use a CRISPR complex known as Cascade (CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense), that contains multiple proteins assembled on the crRNA. Unlike the Type II Cas9 protein, which both recognizes and cleaves the double-stranded DNA targets, Cascade doesn’t have DNA nuclease activity. The DNA cleavage is done by Cas3, a nuclease that, in most cases, is not part of Cascade but is recruited after target binding by Cascade.
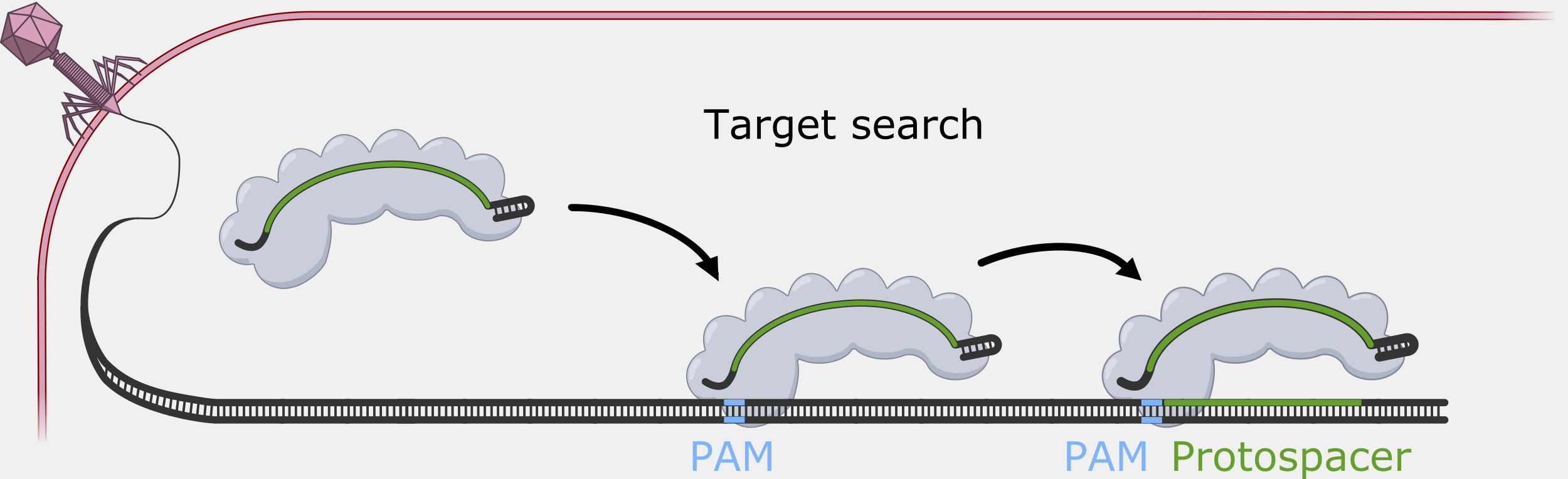
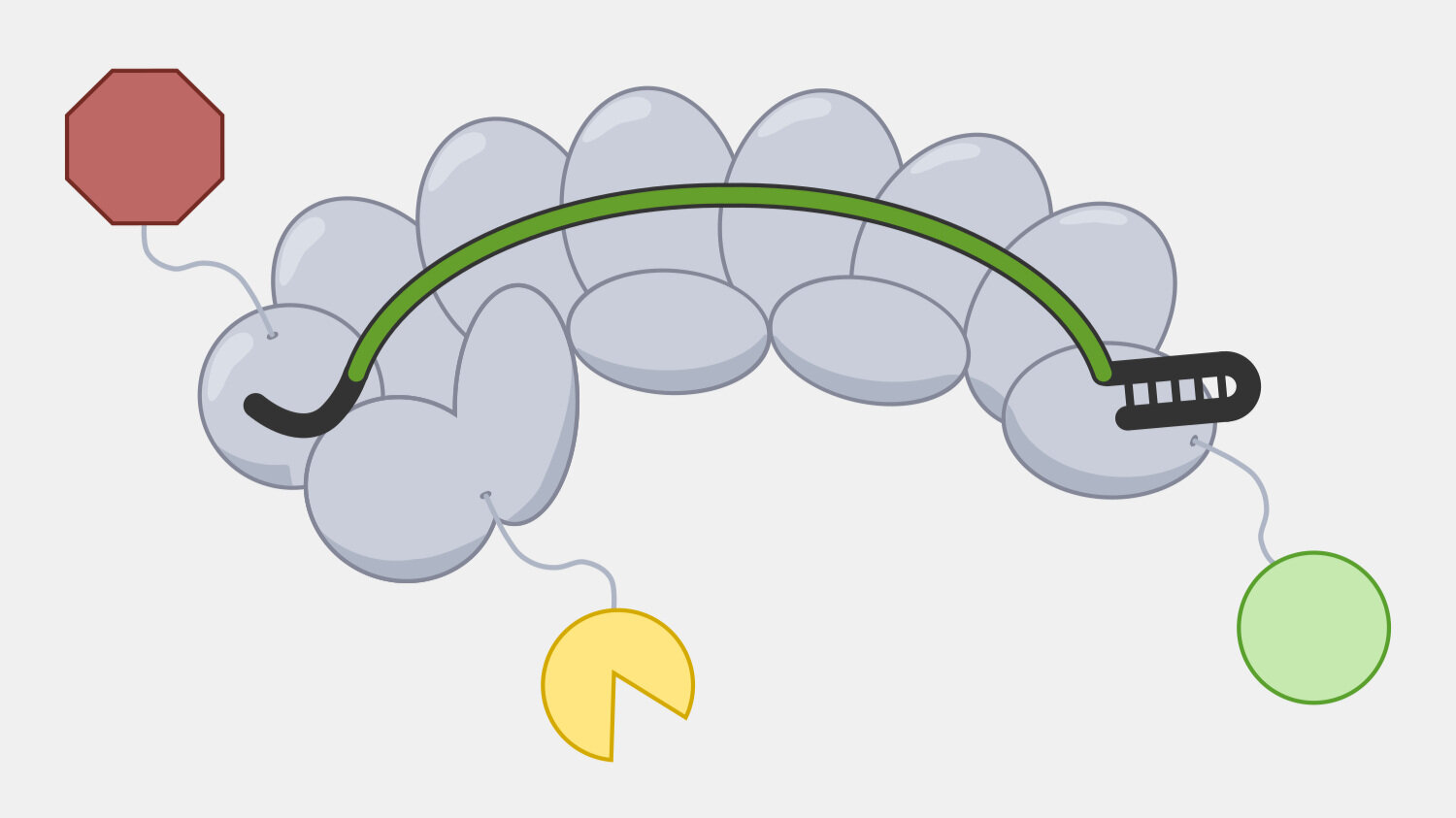
Cascade has to sort through the sea of double-stranded DNA in a cell to find a very specific, and rare, DNA target – a sequence that matches its crRNA. Unwinding all that DNA to check for regions complementary to the crRNA spacer would not be efficient. Instead, Cascade scans double-stranded DNA and binds to locations with a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence.
In the original foreign DNA fragment used to generate the CRISPR array, and the PAM is found next to the protospacer, the sequence that is added as a CRISPR array spacer. Cascade “looks” for the PAM sequence in double-stranded DNA without having to unwind it. Though the PAM sequence is not unique to the phage DNA target, only searching near a PAM significantly reduces the number of locations to unwind.
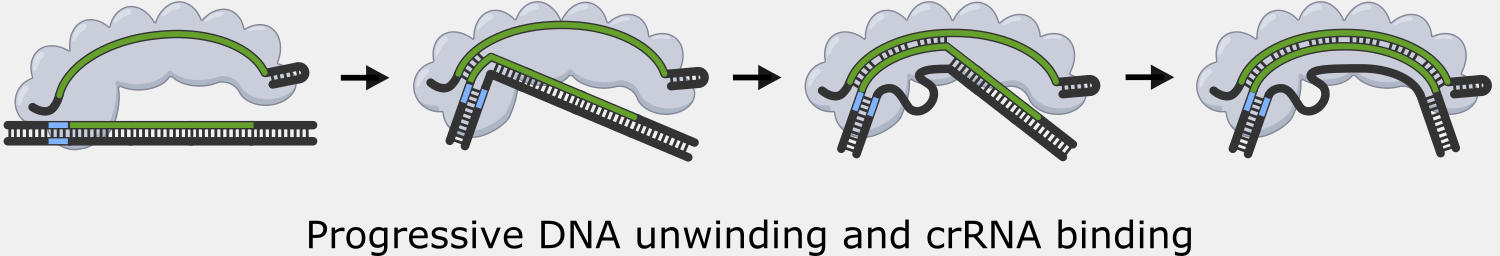
Binding to the PAM causes Cascade to begin unwinding the double-stranded DNA, exposing the target strand. As complementary target strand bases bind to crRNA, the DNA strands continue to separate, and a portion of the now single-stranded non-target strand is spooled out of Cascade.
The PAM binding step also helps reduce the that the CRISPR system would cause autoimmunity by targeting and cleaving the copy of the spacer sequence in the CRISPR array. Though the PAM is part of the original foreign DNA sequence, it is removed when the spacer is inserted into the CRISPR array. This means only the foreign DNA will have a PAM next to the target sequence.
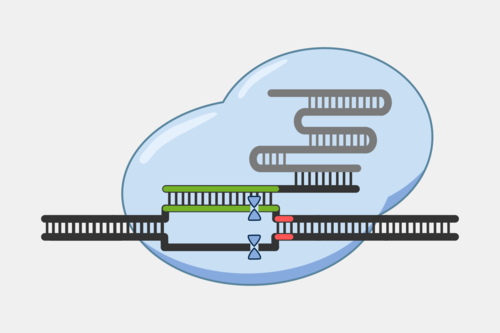
After the Cascade binds the target strand, Cascade recruits Cas3, a protein with both a nuclease and a helicase domain. Cas3 nicks a portion of the exposed non-target strand, activating its helicase activity. With the helicase activated, Cas3 unwinds the DNA and degrades the non-target strand in a 3’ to 5’ direction.
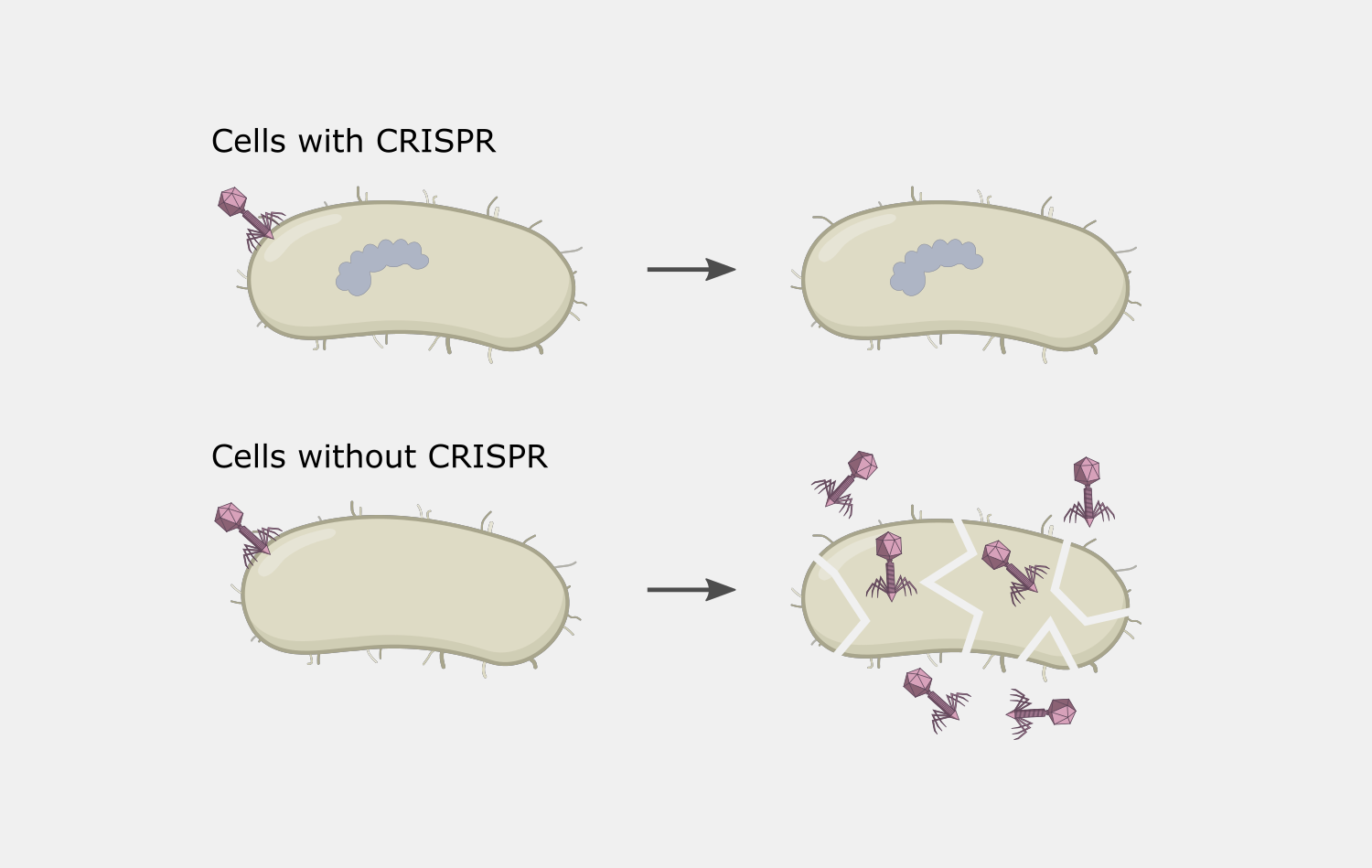
This activity results destruction of the DNA target, blocking the phage infection and providing immunity.
Resources
Related Bailey Lab Research
Using x-ray crystallography, Sabin Mulepati determined a high-resolution structure of Cascade bound to a single-stranded DNA target: Crystal structure of a CRISPR RNA-guided surveillance complex bound to a ssDNA target. Mulepati, Heroux and Bailey, 2014, Science
Using purified components of a Type I system from E. coli, Sabin Mulepati and Scott Bailey showed that Cas3 nicks a single strand of DNA and the degrades in a unidirectional manner, 3’ to 5’: In vitro Reconstitution of the Escherichia coli RNA-guided Immune System Reveals Unidirectional, ATP-dependent degradation of DNA target. Mulepati and Bailey, 2013, J. Biol. Chem. PDF
Sabin Mulepati, Amber Orr and Scott Bailey determined the structure of CasA, the largest Cascade subunit, and demonstrated that it is required for Cascade’s DNA binding: Crystal Structure of the Largest Subunit of a Bacterial RNA-guided Immune Complex and its Role in DNA Target Binding. Mulepati, Orr and Bailey, 2012, J. Biol. Chem. PDF
Sabin Mulepati and Scott Bailey used a truncated version of Cas3 to determine the structure of the HD domain and characterize its metal ion-dependent single-strand nuclease activity: Structural and biochemical analysis of the nuclease domain of the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) associated protein 3 (Cas3). Mulepati and Bailey, 2011, J. Biol. Chem. PDF
Reviews
Harnessing “A Billion Years of Experimentation”: The Ongoing Exploration and Exploitation of CRISPR–Cas Immune Systems, Klompe and Sterberg, 2018. The CRISPR Journal
The Biology of CRISPR-Cas: Backward and Forward, Hille et al, 2018. Cell